Electric Vehicles (EVs) are automobiles that are powered by electric motors, using electricity as their primary source of energy. They offer an alternative to vehicles with internal combustion engines (ICEs) that rely on fossil fuels. Instead of internal combustions engine they use electric motor and battery propulsion.
EVs have gained significant popularity due to their environmental benefits, energy efficiency, and advancements in technology.
How does an Electric Vehicle Work?
It is completely different mechanism from conventional gasoline power engine. Following are some different parts of electric vehicle.
- Electric Motor.
- Reducer Gear Box.
- Electric Power control Unit.
- Regenerative braking systems.
- Battery.
- Charging Unit.
Electric Motor:

- The main function of electric vehicle motor is to covert the electric energy of battery in the mechanical energy or rotational energy.
- Electric motor play important role in electric vehicle as it is replacing vehicles engine, and it is responsible for propulsion of electric vehicle. This electric motor takes power from the vehicle battery pack and motor coverts in mechanical energy or rotational energy this energy is transferred to the vehicle.
- Motor is not only mechanical energy but it also works as the power generator while deceleration, that with help of regenerative breaking it recovers some of the kinetic energy from wheels, In regenerative breaking energy of breaking in not only converted into heat but it also converted in electricity.
- Electric motor provides stable and smoot power to the wheels reduce noise and vibration which gives comfortable ride to vehicles passenger.
Reducer Gear Box
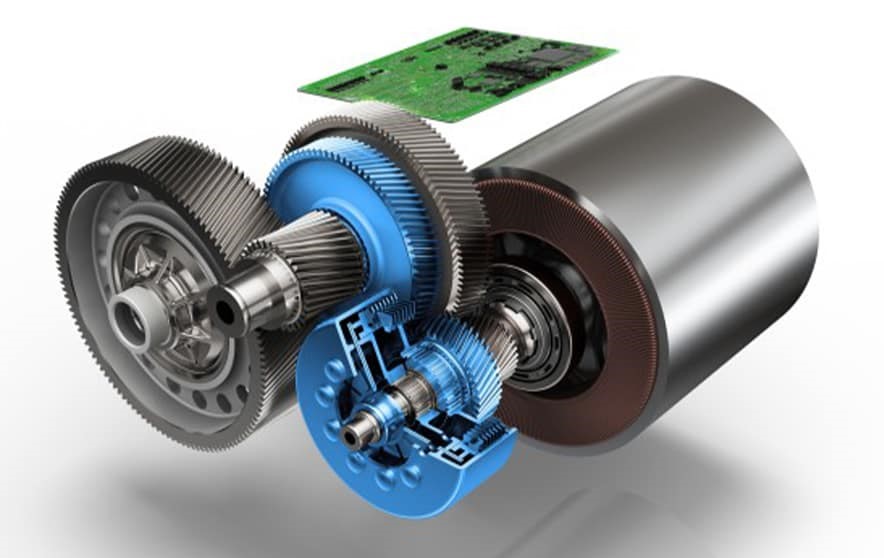

- As we all know induction motor have a rotor speed of 18000 revolution per minute (RPM) due this we cannot connect motor to the wheels and also to get variable differential action of wheels while Turing on road.
- In electric vehicle electric vehicles it uses single speed transmission and open differential is used to drive wheels.
- In conventional vehicle gear box is used with multiple gear ratios, to achieve different speeds and torque electric vehicle uses reducer gear box or gear train.
- All electric vehicles have an automatic transmission and also an electronic control system.
Electronic Power Control Unit
Electronic power control unit is combination of inverter, converter system which is used for two different operations in electric vehicle as described below.
- Electronic power control unit includes inverter systems to convert direct current (DC) from battery into alternating current.
- This electronic power control unit is also used to transform wheels Kinect energy into electric energy while regenerative braking which is used to charge the battery pack of electric vehicles
- Electronic power control unit controls the motor speed so that we can get different speeds while driving the vehicle. Power control unit plays an important role in electric vehicle as it is used to control electric power from the battery pack.
Regenerative Braking System
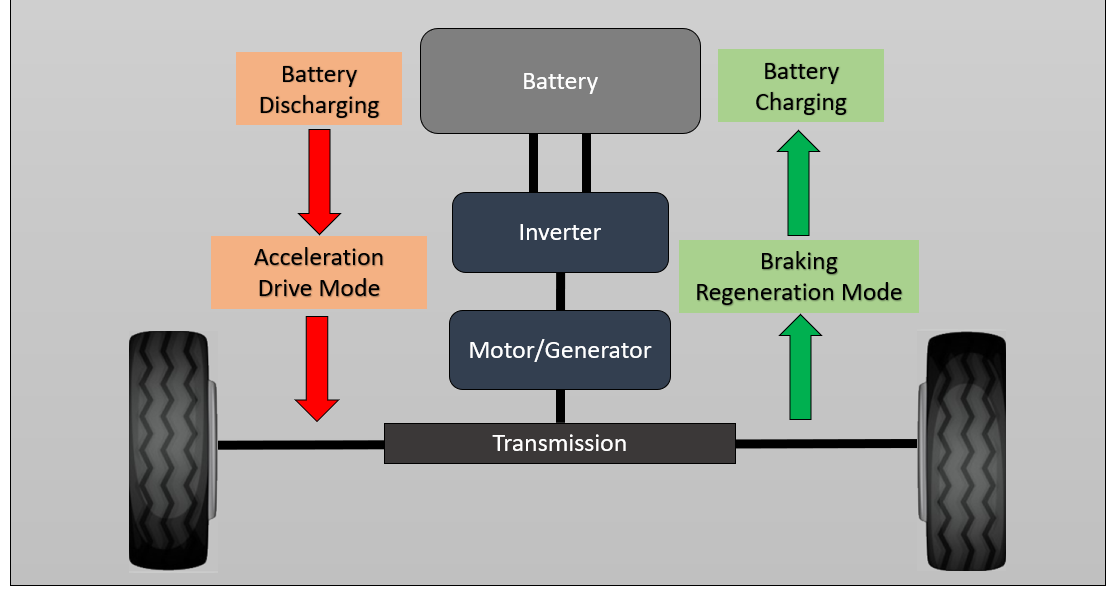
Regenerative braking system is used to slowing down speed of vehicle and also it acts as energy generator. When driver removes legs from acceleration paddle reverse action starts that is kinetic energy of vehicles wheel transferred back to the electric motor.
- In Regenerative braking system power control unit controls the power supply to the stator so that is act as stable magnet.
- When wheels kinetic energy is used to drive the rotor in magnetic field this start to generate electric power which is further through power control unit used to charge vehicles batteries.
- Regenerative braking system increases efficiency and drive range by utilizing kinetic energy of wheels.
Battery

- Electric vehicle battery is used to store electrical energy which is used to drive a vehicle.
- Battery plays an important role in electric vehicle as are main source of energy to the vehicles motor. Electric vehicle battery is pack of rechargeable cells. The combined cells are called battery pack.
- Electric batteries are completely different from usual starting, lighting and ignition batteries.
- Electric batteries are relatively lighter in weight which reduce electric vehicles weight and increase their efficiency.
- Electric vehicle battery is made of lithium-ion they are specifically designed for high energy storage capacity and also to manage number of cycles of recharge.
Charging Unit
- A charging unit is a part of power control unit which is used to charge battery pack of electric vehicle.
- This unit includes invertor part of power control system. Charging unit is used to convert alternating current into direct current through the inverter. This converted electric power is used to charge the battery pack of vehicle.
- Using this charging unit, we can charge our electric vehicle at house hold power supply and also at electric charging stations.
Types of electric vehicles (EVs)
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): These vehicles are solely powered by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries. BEVs do not have a traditional internal combustion engine and produce zero tailpipe emissions. They offer a fully electric driving experience and require external charging infrastructure to recharge their batteries.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): HEVs also combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine, but they cannot be charged externally. The electric motor assists the engine during acceleration and recaptures energy through regenerative braking. HEVs primarily rely on gasoline or another fuel and do not offer all-electric driving capabilities.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): PHEVs combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine. They have a rechargeable battery pack that can be charged from an external power source, allowing for a certain all-electric driving range. Once the battery is depleted, the PHEV can switch to the internal combustion engine or alternate fuel for extended range.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): FCEVs use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers the electric motor. Hydrogen is stored in onboard tanks and reacts with oxygen from the air in the fuel cell to produce electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. FCEVs are still in the early stages of commercialization and face infrastructure challenges.
What are the advantages of electric vehicle?
- Environmental Benefits: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving local air quality. They contribute to mitigating climate change and decreasing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs are more energy-efficient compared to ICE vehicles. Electric motors convert a higher percentage of energy from the battery to power the wheels, while ICEs waste energy as heat.
- Lower Operating Costs: EVs have lower operating costs due to the relatively lower cost of electricity compared to gasoline. Additionally, electric motors have fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance requirements.
- Regenerative Braking: EVs utilize regenerative braking, which recaptures energy during braking and deceleration, converting it into electricity to recharge the battery. This feature improves efficiency and extends the driving range.
- Home Charging Convenience: BEV owners can charge their vehicles at home using dedicated home charging stations, providing convenience and eliminating the need for frequent visits to public charging stations.
What are the disadvantages of electric vehicle?
- Drive Range: The limited driving range of some EVs and the availability of charging infrastructure may cause concerns about running out of battery power, known as range anxiety. However, the range of EVs has been improving with advancements in battery technology.
- Charging Stations Structures : The development of a robust charging infrastructure is essential for the widespread adoption of EVs. Governments, businesses, and utility companies are investing in the expansion of public charging networks to address this challenge.
- Battery Technology: The cost, energy density, and charging speed of batteries are crucial factors for the success of EVs. Ongoing research and development aim to improve battery technology, including the advancement of solid-state batteries with higher energy density and faster charging capabilities.
- Transitioning Grid: The increased demand for electricity due to widespread EV adoption poses challenges for the electrical grid. Managing charging load, integrating renewable energy sources, and implementing smart grid solutions are necessary to ensure a reliable and sustainable charging infrastructure.
- Affordability: The upfront cost of EVs is currently higher than that of comparable ICE vehicles, primarily due to the cost of battery technology. However, prices have been decreasing, and various incentives and subsidies are available to promote EV affordability.
Conclusion:
Overall, EVs are a promising and rapidly evolving technology that offers a cleaner and more sustainable transportation alternative. Continued advancements and supportive policies are expected to further enhance their adoption and address the remaining challenges.
